SDN the latest trend in Data Centers

What is an SDN?
Software-defined networking (SDN) is an approach to computer networking that allows network administrators to manage network services through abstraction of higher-level functionality.
This is done by separating the system that takes decisions about where traffic is sent (the control plane) from the underlying systems that forward traffic to the selected destination (the data plane). As this article claims, this is one of the latest trends in Data Centers
SDN is an architecture purporting to be dynamic, manageable, cost-effective, and adaptable, seeking to be suitable for the high-bandwidth, dynamic nature of today's applications.
Why do modern Data Centers need a new networking architecture?
Some of the key computing trends driving the need for a new network paradigm include:
- Changing traffic patterns
- The "consumerization of IT"
- The rise of cloud services
- "Big data" means more bandwidth
Which are the main difference between SDN and traditional network models?
- Traditional Networking
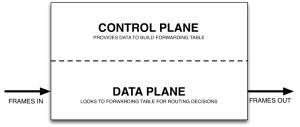
The following graphic above is roughly how a network device functions. Network Devices have a control plane that provides information used to build a forwarding table. They also consist of a data plane that consults the forwarding table. The forwarding table is used by the network device to make a decision on where to send frames or packets entering the device. Both of these planes exist directly on the networking device
- Software Defined Networking
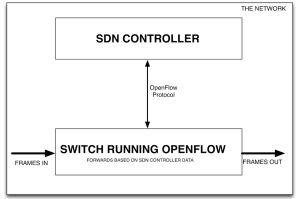
Software Defined Networking abstracts this concept, and places the Control Plane functions on a controller. The SDN controller can be a server running SDN software. The Controller communicates with a physical or virtual switch Data Plane through a protocol called OpenFlow. OpenFlow conveys the instructions to the data plane on how to forward data. The network device must run the OpenFlow protocol for this to be possible. You can see how SDN differs from traditional networking in the following graphic.
Which are the main benefits
The OpenFlow protocol is a foundational element for building SDN solutions. This architecture is:
Directly programmable: Network control is directly programmable because it is decoupled from forwarding functions.
Agile: Abstracting control from forwarding lets administrators dynamically adjust network-wide traffic flow to meet changing needs.
Centrally managed: Network intelligence is (logically) centralized in software-based SDN controllers that maintain a global view of the network, which appears to applications and policy engines as a single, logical switch.
Programmatically configured: it lets network managers configure, manage, secure, and optimize network resources very quickly via dynamic, automated SDN programs, which they can write themselves because the programs do not depend on proprietary software.
Open standards-based and vendor-neutral: When implemented through open standards, SDN simplifies network design and operation because instructions are provided by SDN controllers instead of multiple, vendor-specific devices and protocols.
Implementations
For more information we suggest reading Network Virtualization For Dummies by VMware