Network Requirements Solutions

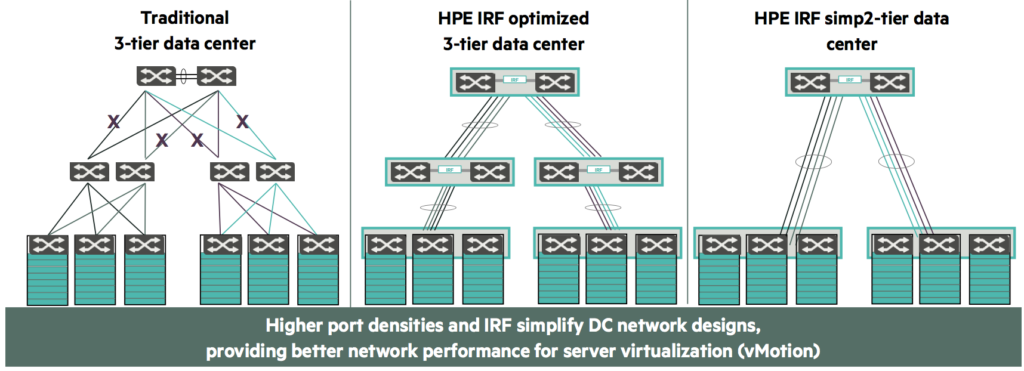
Hi everybody! Today we are going to talk about network requirements solutions for our Data Center offered by HP, trying to explain them deeper than in previous posts. First, we are going to review the network redundancy, load balancing and loop prevention. As we all know at this point, it is very critical for bank institutions the Single Point of Failue (SPF) avoidance. In order to achieve it, all network devices must be redundantly connected so our data and operation keep save and continue working after a failure occurs. Once, redundancy is implemented, it is clear to see that loops in the same broadcast domain will be created because there will be different paths to reach the same gateway. This device disposition might create broadcast storms which can collapse the network, so loops must be avoided. The most common solution to this is the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), but it is not suitable for Data Centers given that 50% of ports are blocked, so the overall network performance decreases. Moreover, because of the desire to use all redundant links and be more efficient, load balancing is also required to get all paths working and being useful. The solution to all of these requirements that HP offers is an all-in-one technology called Intelligent Resilient Framework (IRF). It is a network virtualisation technology that allows the interconnection of multiple devices through physical IRF interfaces that combine them in a way that they are seem as a single logical device (switch, router, etc.) from other devices view. Thanks to it, all the devices in the same IRF group need to be configured only once, and this configuration will be automatically applied to all devices. When used with Link Aggregation Protocol (LACP), several parallel links between devices can be formed, achieving an on-demand and scalable performance boost. Moreover, the virtualization to a single logical device allows the avoidance of loop prevention and redundancy protocols such as STP, MSTP, RSTP, VRRL, LACP, etc. because these functionalities are performed by itself. Also, virtualized systems, by definition, provide load balancing mechanisms between member devices, thus fully utilizing available bandwidth. Furthermore, IP addressing becomes simpler because all member devices of the IRF group will only need one single IP address to be managed and perform packet forwarding. The difference between a traditional STP network and an IRF optimized network is show in the image below. If you want to learn more about IRF, click here.
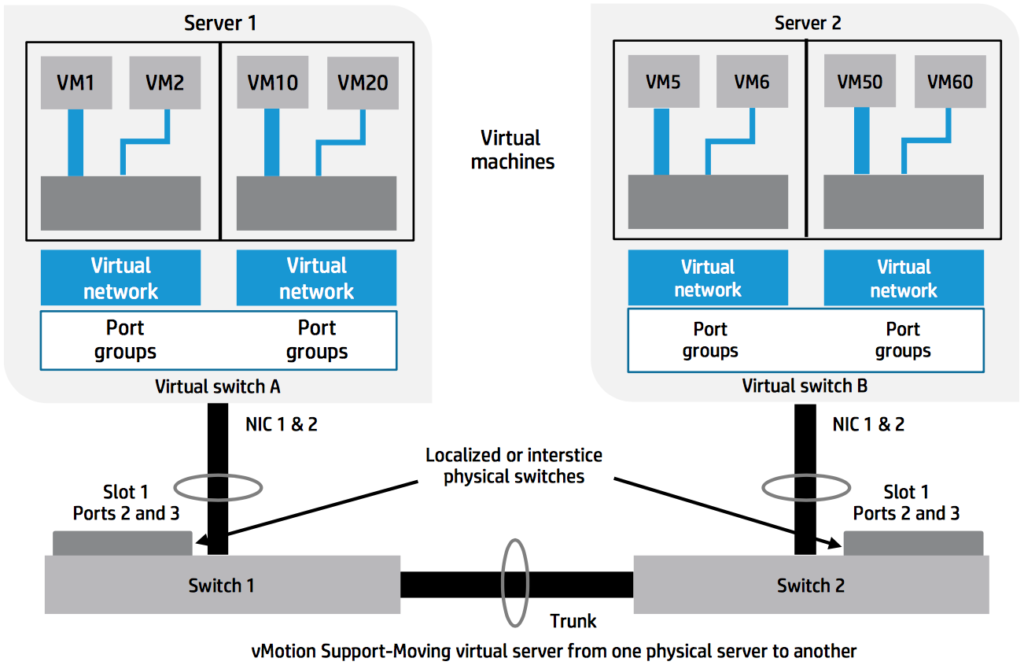
The next requirement is the capability to isolate application and data networks from email and Internet access networks, as well as isolating them from management and backup networks. Virtualisation is the key point. On one hand, the use of Virtual Machines provides a way to have a lot of mobility and scalability and share the same physical resources for different purpose instances while segmenting them into L3 independent networks.
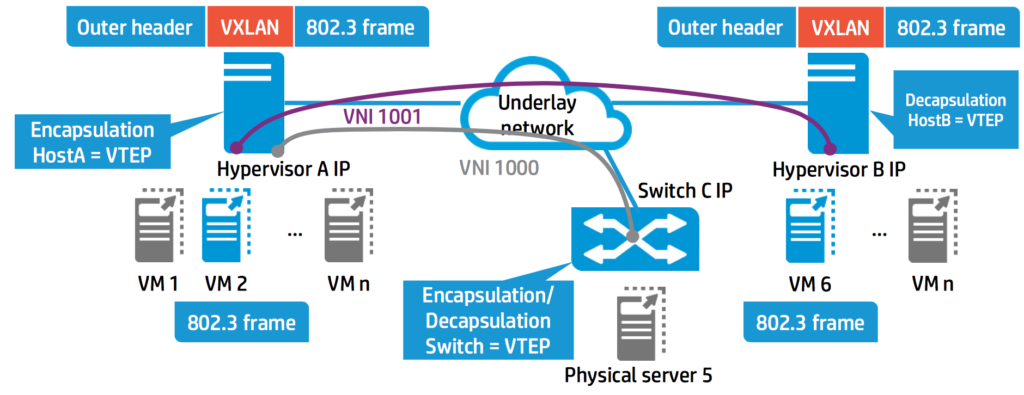
The interconnection and isolation of VMs is achieved thanks to VXLAN protocol, which is used in the overlaid architecture we propose. Communication between VMs are established with Virtual Tunnel Endpoints (VTEP), encapsulating layer 2 MAC frames into a UDP header. These VXLAN frames only carry a 54-byte overhead, and use VXLAN Network Identifier (VNI) to isolate the traffic, supporting up to 16 million LAN Segments, which is much higher than the 4094 limit imposed by the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN standard.
When this is combined with an SDN architecture, management of the Data Center turns much simpler. SDN offers an easier, more dynamic interaction with the network through a “clean” interface obtained through abstraction of the control plane. This reduces the complexity of managing, provisioning, and changing the network. The convergence of SDN and Virtualization is achieved with the HP VMWare NSX framework. It provides a complete network virtualization for the Software-dDfined Data Center and helps the automation of provisioning of custom, multitier network topologies. NSX creates an overlay network which provisions virtual networking environments while avoiding CLIs or manual administrator intervention. The virtual overlay network abstracts the network operations from the underlying hardware, just like server virtualization does for processing power and operating systems. Here you can learn more about VMWare NSX. Finally, speed requirements claim a 1 Gbps guaranteed bandwidth for mail service and 4 Gbps for the other services, which can be upgraded in the future. Also, Gigabit Ethernet technology 10 Gigabit Ethernet links are wanted, while the equipment, if possible, must support 40G and 100G speeds for a near future. This is not a problem because HP solutions consider the use of dark fibre to interconnect network devices, which adopts the IEEE standards for Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet over single-mode fibre. In addition, current HP network devices have Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet ports which perfectly fit these requirements. For more information about the network devices, you can consult our other today’s post. Furthermore, HP claims that VXLAN and IRF technologies are already designed to support 40G and 100G technologies, so they won’t become deprecated and the same solution will still be suitable. Thank you for reading us again, if you liked this post feel free to comment and share it! See you next week!