Datacenter Location and Facilities Design

Anyone who has studied networks or has a minimum knowledge about them, knows that there are two worlds that coexist in each one of them. Every network is structured in a logical and a physical pane.
The logical pane ends up to be the most important or at least the one an IT expert uses the most. Logical drawings show us how is the network grouped and the interconnection between its elements inside: what are the IPs assigned, the vlans if there are any, what are the relationship between hosts or if they can even talk to each other. When focusing in data center environments this effect gets even more noticeable. We are talking about virtualization of hosts, the abstraction of our network from its physical structure.
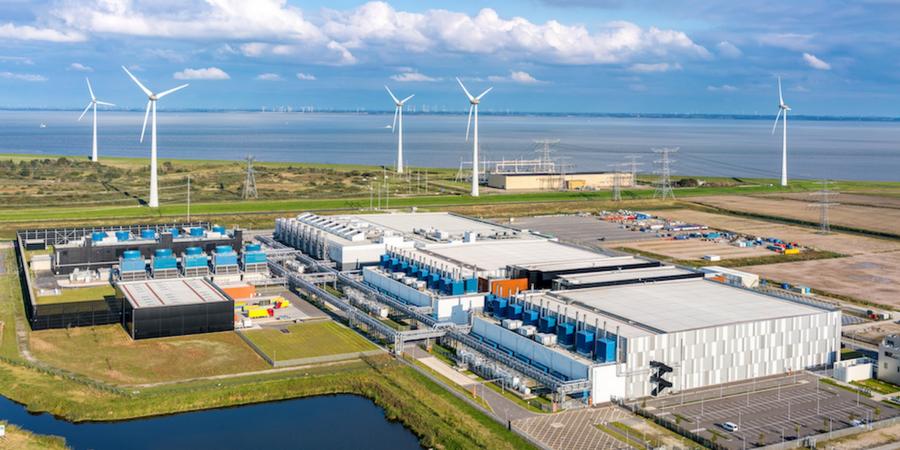
But sure we have to remember that a datacentre, doesn’t matter if it’s on premise, cloud based or hybrid, at the end of the day it is an array of racks placed somewhere in a building or a warehouse.
A good planning design of the site and its facilities can be equally important as any other design step in a datacenter. It doesn’t matter if you have full redundancy layout in your servers if you don’t have a redundancy plan for your electrical supply or you suffer from a flood.
Some of the major aspects to consider when designing datacenter facilities are:
- Electrical: It is a must, to control what your electrical needs are at the moment, but also keeping in mind a possible growth in the future. An uninterruptible power supplier and a redundant PDU system are the key points of a good electrical design. Furthermore, a diesel generator and a fuel tank, sized depending on your needs, will keep the system running in case of electrical emergencies.
- Mechanical: Devices consistently running, like we see in a datacenter environment, generate heat. Cooling, heating and humidification parameters must be controlled for people being able to work in the facilities. Also it’s important to continuously filter particle levels in the air.
- Disaster Protection: Disasters like fires, floods, tornados, etc. can happen and a datacenter must be prepared and protected against them. Smoke detection, pre-action wet systems, earthquake-proof buildings, raised floors…
- Security: Datacenter infrastructure and devices aren’t cheap and are at high risk of stealing. A good perimeter and access control keeps logs of every person with access to the facilities.
- Communication: Of course, a datacenter is all about the transmission and sharing of data. A good, redundant, communication system of a trustworthy supplier is key.
- Location: Location is one of the most important aspects. It determines the access to all our points explained before, a good physical communication system for shipping and workers, but not near residential or other sound-sensitive users, an adequate site for at-grade development, etcetera. Politics are also involved: taxes, public incentives, data security regulations, and much more.
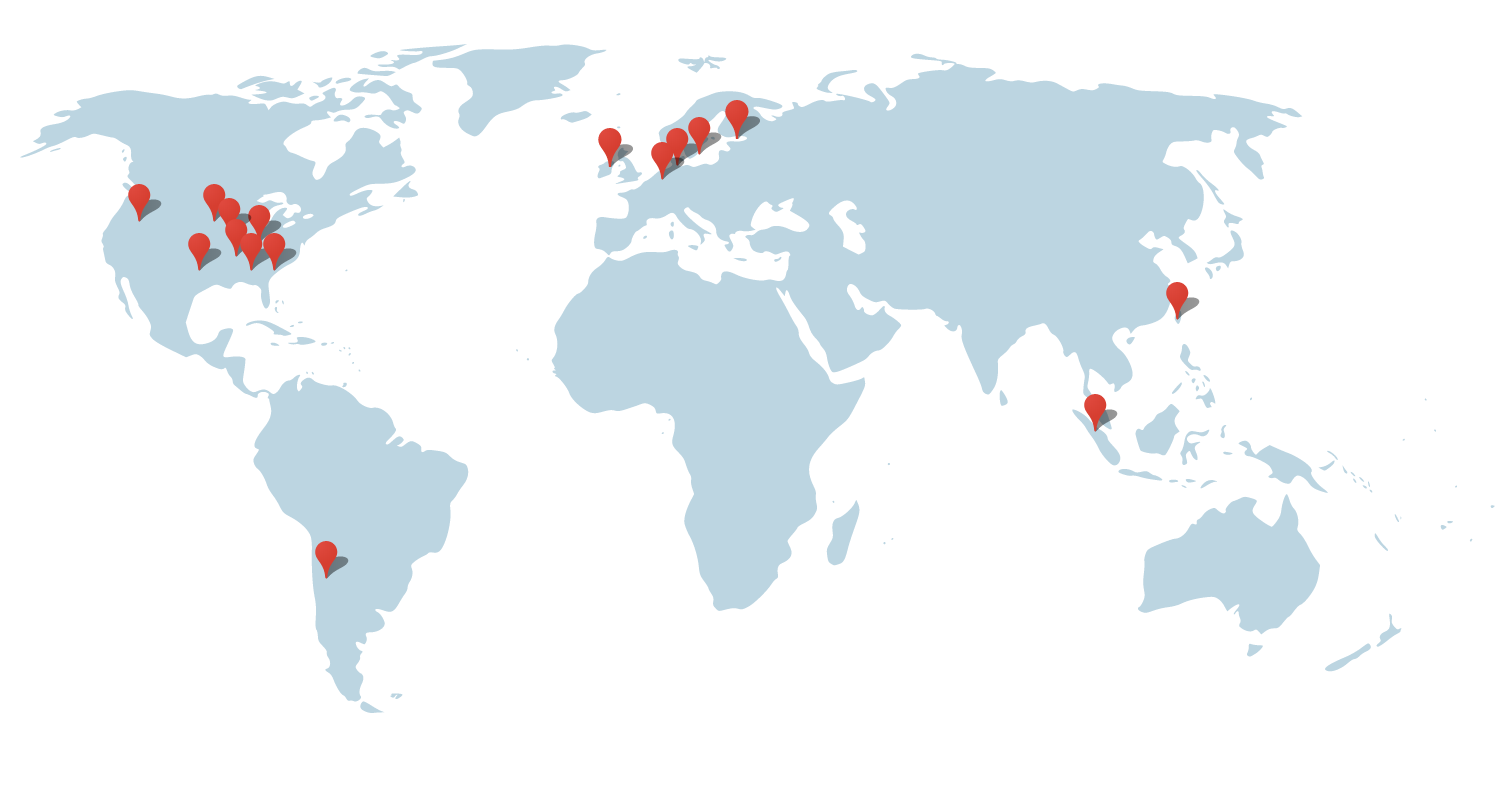
To give an example, here we can see the map of google datacenter locations around the globe:
Albert Ribas Sanchez.