The Hypervisor

A hypervisor is a system capable of creating virtual machine and allocate resources to it. The main objective of creating virtual machines is being able to share the resources of one server between multiple servers.
How does it work?
Some of the interesting tasks that virtual machines are used in are data replication, server consolidation, desktop virtualization and cloud computing. Hypervisor helps in the task of replicating a virtual machine. It enables selecting the parts of the virtual machine you want to replicate, so you do not have to replicate the whole virtual machine.
Moreover, when having multiple servers operating different services for customers over the internet, managing them all becomes a difficult task. The hypervisor facilitates the management by being able to manage them all in one physical machine. Nevertheless, they operate more efficiently because the resources of the physical machine won’t be idle while they are not in use. The hypervisor will allocate these resources to the virtual machines.
Another potential of virtualization is being able to run an application that only runs in one operating system different from the one you have in the physical machine. For instance, if having a Mac OS and wanting to run a specific software only available for Windows OS, that can be possible without having to change the OS of the physical machine. It would be as easy as having a virtual machine with Windows OS and running that software in the virtual machine.
What is it used for?
One of the main benefits is that if a virtual machine crashes, it won’t affect the others. Moreover, the system can implement ways to simply start running another one, so the service will only stop for a few minutes. That is because although they use the same physical hardware, they are logically separated from each other.
Also, security is a key plus of virtual machines. As the hypervisor creates a layer between the virtual machine and the physical OS, in case a malicious file was downloaded in the virtual machine it will only affect the virtual machine and not the primary OS.
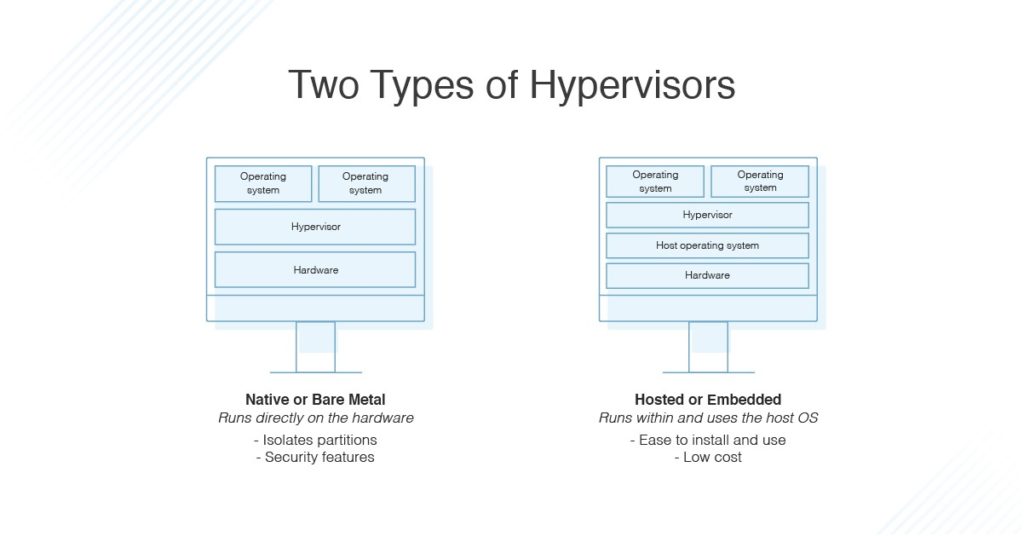
Types of Hypervisors
- Native or “bare metal” hypervisors
- Hosted or “embedded” hypervisors
A bare metal hypervisor is installed directly on the hardware of your machine, whereas a hosted hypervisor is installed on your operating system. Bare metal hypervisors thanks to having direct access to the underlying hardware are faster and more efficient. However, hosted hypervisors are easier to use as they are more user-friendly. An example of them is VMware.
Anna Gutiérrez y Marco Pérez