The JOURNAL OF SUSTAINABILITY published “USER ACCEPTANCE OF MOBILE APPS FOR RESTAURANTS: AN EXPANDED AND EXTENDED UTAUT-2” by Ramon Palau-Saumell, Santiago Forgas-Coll, Javier Sánchez-García, and Emilio Robres
Concerning the context of this study, in Spain, before the pandemic, the hospitality sector represented 6,4% of the Gross Domestic Product and employed 1,7 million workers (INE, 2020). With respect to the technology of mobile applications, in 2021 Spanish people spent 3,6 hours per day on mobile internet (comScore, 2020). Nearly 90% of the mobile internet time was spent on mobile applications (eMarketer, 2020).
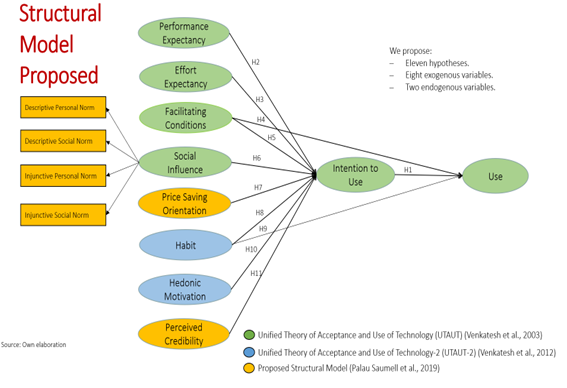
Regarding the concept of Technology Adoption. Technology Adoption is defined by the literature as the stage of choosing a technology for use by an individual or an organization. The adoption of technology has been studied using different theoretical models being this field of research very mature. Accordingly, this research utilized the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology 2 as a theoretical framework because it is a review of the most significant models in the field and for its greater predictive power.
Consequently, the questions that were investigated in this research are the following:
-
What drivers facilitate Spanish people to use Mobile Apps for Searching and Booking Restaurants, and what is their level of importance?
-
Are there any significant differences in terms of gender, age, and experience that influence those drivers?
In relation to the data collection and the method of analysis, 1200 were collected using a non-probabilistic sampling method, and 11 hypotheses were proposed (moderation hypotheses not included). Hypotheses were tested using structural equation models with the statistical software EQS 6,1.
The results of the SEM analysis of the structural model indicated that intentions to use, facilitating conditions, and habit significantly and positively influenced use. In addition, performance expectancy, effort expectancy, facilitating conditions, hedonic motivation, price-saving orientation, habit, social influence, and perceived credibility significantly and positively affect the intentions to use.
Finally, a moderation effect analysis was conducted to test the moderation hypotheses (not depicted in the path diagram). The results showed that gender and age did not moderate the effects of the independent variables on intention to use. Nevertheless, this research identified significant differences in the moderating effect of experience in using mobile applications for restaurant search and booking between facilitating conditions and use, intentions to use and use, and habit and use.
In sum, the findings strongly supported the appropriateness of the model proposed for the understanding of the factors that are involved in users’ acceptance of mobile apps for restaurant search and booking.
Please feel free to read the full article at https://doi.org/10.3390/su11041210
Author: Emilio Robres