Edge computing

Over the years, the number of connected devices and therefore the volume of information that needs to be processed has grown exponentially, which means that datacenters must have higher processing capabilities and more storage available. These problems can be easily solved by increasing the number of servers, improving the connections... up to a certain point. And even then, there is still a problem: datacenters are “centralized”, not always close to the users, which brings issues that some applications cannot afford.


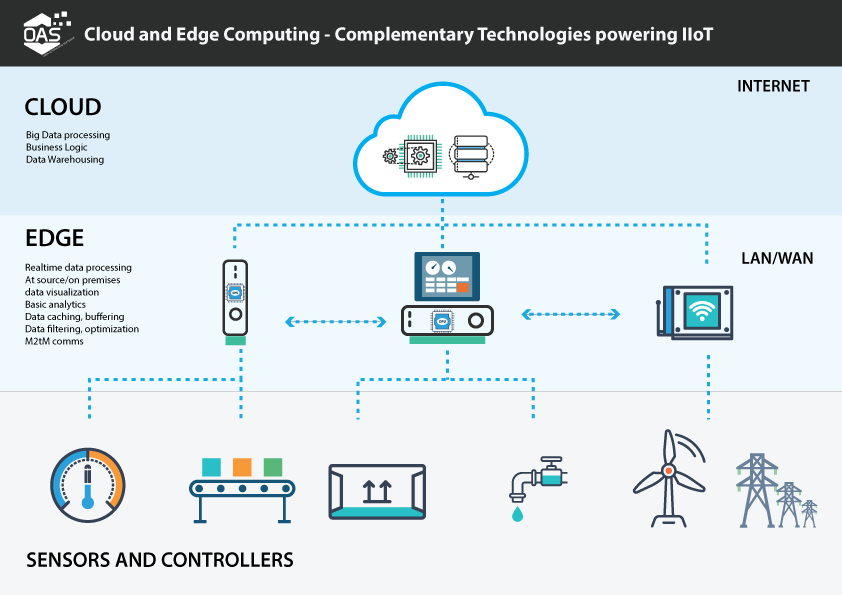
Edge computing has the ability to answer all these problems: It is the practice of processing data near the edge of the network, where the data is being generated, instead of doing so in a centralized data-processing warehouse. In other words, information is processed by the device itself or a local computer or server (local datacenter). The point of this is that data is not transmitted throughout the internet to the datacenter for processing and neither is the response sent back to the origin: data is generated, handled and stored locally (depends).
This practice means the creation of a sort of “distributed mesh network of microdata centers”, which features decentralized processing power and enables, amongst others, The Internet of Things (IoT).
Representation of Edge Computing:
In using a completely different method of handling data, some advantages and disadvantages appear:
Advantages:
Speed
Processing units are now closer to the data source, and in doing so, latency is drastically reduced. That enables real-time data processing and transmission. Self-driving cars, among others, benefit a lot from this practice, to the point that they would not exist without it: they need real-time computing.
Reduced data throughput
Only data that cannot be evaluated locally or that should be stored in the datacentre is sent, most of it is processed locally. That reduces the strain on the datacenter and the use of network bandwidth.
Security
Most information does not leave the local network, meaning it cannot be intercepted in the first place (That is also a disadvantage, it will be explained later). Moreover, as a decentralized system, it is especially resistant to DDoS and power outages, amongst others.
Scalability
Given that the nature of edge computing is intrinsically linked to decentralized and distributed systems, it is no surprise that edge computing creates scalable systems (an inherent advantage of distributed/decentralized systems): It is merely a matter of adding more devices, which do not require substantial bandwidth and thus network resources.
Reliability
Edge computing means processing near the origin, and that in turn means less chance of network failure between the processing unit and the critical data.
Disadvantages:
Processing limitations
Data is computed and stored (depends) in the edge nodes, a place which by default has not the storage and processing power of Cloud Computing. As such, edge computing cannot deal with huge amounts of information.
Programming
Unlike in the Cloud, where programs are compiled to run for a specific platform or a set of them, in Edge Computing they can run on different platforms, making the creation of applications challenging in this environment.
Scheduling policy
Scheduling processes between the different edge nodes can also be a challenge: you have to consider if a certain node is capable of doing the task and if that would not affect its actual performance.
Security
Edge nodes have weaker security and can be used to gain access to the whole system, as there is not a powerful centralized security structure. Policies need to be implemented to prevent new types of attacks.
Conclusion
Edge Computing will not be a replacement for Cloud Computing, but a supplement. While Edge Computing is more suitable for processing a small set of information with speed (due to its properties), Cloud computing still needs to be used for dealing with large datasets. This way, at least, some Datacenters will be freed from certain tasks, gaining in efficiency.