Efficient multimedia data clustering thanks to parallel consensus architectures

Machine learning offers scientists a broad range of tools to discover meaningful patterns in data. Among them, unsupervised classification (also known as clustering) allows to reveal underlying group structures with no need for labelled training data. For this reason, clustering is used to solve a wide range of different problems, like spam filtering, fake news detection, or document analysis, to name a few.
However, when clustering is applied on multimedia data –that is, data that is simultaneously expressed in several modalities, such as image, text, audio, etc.-, multiple questions arise, such as i) should one modality dominate the clustering process?, ii) if so, which one, and to what extent?, iii) should the modalities be fused?, or iv) if so, how should the fusion process be conducted?
To solve this problem, GTM researchers Xavier Sevillano, Joan Claudi Socoró and Francesc Alías designed hierarchical consensus architectures, a brand new approach to tackle unsupervised multimedia data classification using consensus clustering –a strategy to combine multiple clustering systems.
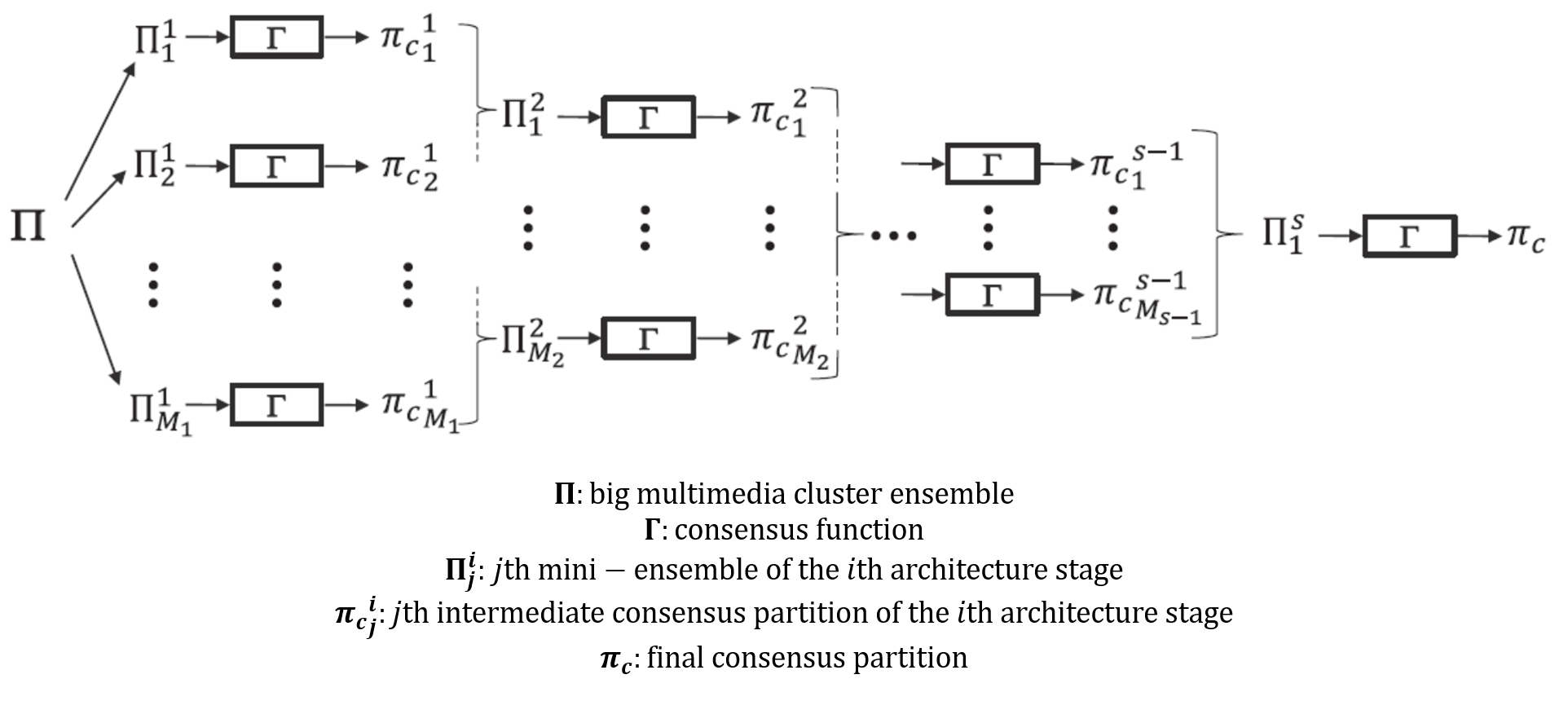
The advantage of hierarchical consensus architectures is twofold: on the one hand, they enable clustering practitioners to conduct multimedia data clustering in a robust way without worrying about finding the optimal setup for the data at hand (i.e. the most suitable clustering algorithm, the most adequate data representation, and so on). And on the other hand, their inherent parallel nature allows to reduce dramatically the execution time of consensus clustering.
In a recent article published at the Information Sciences journal (https://www.journals.elsevier.com/information-sciences), one of the highest-ranked journals in computer science, the authors presented a theoretical study of the computational complexity of parallel hierarchical consensus architectures. This analysis was complemented with a set of experiments conducted on several multimedia data sets. The results validated the computational efficiency of the proposal, which outperforms traditional flat consensus by a wide margin. Moreover, the proposed approach also allows to obtain high quality clustering results, thus paving the way to robust and efficient multimedia data clustering.
Sevillano, X., Socoró, J.C. & Alías, F. (2020) Parallel hierarchical architectures for efficient consensus clustering on big multimedia cluster ensembles. Information Sciences, 511:212-228. DOI: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.09.064. Online version of the paper at https://authors.elsevier.com/a/1Zq2k4ZQDzm5m