GTM collaborates in the application of deep learning and computer vision to medicine: the diagnosis of pressure ulcers
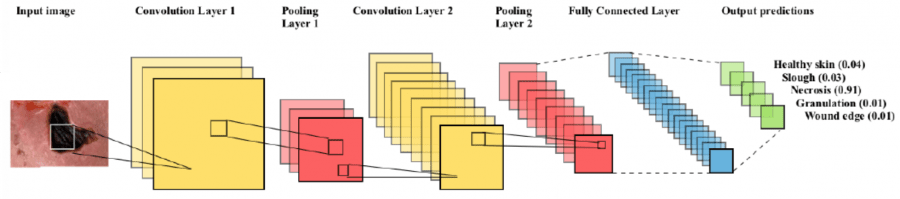
Since 2017, GTM researchers Xavier Sevillano and Alejandro González collaborate with the University of Deusto, Georgetown University and the University of Louisville in the research of non-invasive tools for the diagnosis of pressure ulcers based on computer vision and deep learning techniques.
Pressure ulcers are a type of chronic wounds resulting from damage caused by pressure over time causing an ischemia of underlying skin structures, and are often suffered by long time care patients subject to lengthy periods of immobilization.
According to recent studies, more than 2.5 million people in the United States develop pressure injuries, and the risk of developing them during hospital stays is 3 times greater than the risk of being involved in a car accident.
Pressure ulcers are painful and prone to infection, so to avoid the discomfort of patients during the diagnosis and monitoring processes, non-invasive techniques are preferred. In this sense, imaging techniques are called to play a key role, as they allow an accurate analysis of its features with no need of contact with the wound itself.
The joint work between the aforementioned research centers, which has been funded during three consecutive years by the Aristos Campus Mundus initiative, has resulted in the publication of a comprehensive review of state-of-the-art imaging techniques applied on pressure ulcer image analysis, and a prospective study of the possibility for deep learning to outperform these techniques.
This work has been published in the prestigious Artificial Intelligence in Medicine journal, which publishes works on interdisciplinary perspectives concerning the theory and practice of artificial intelligence in medicine, medically-oriented human biology, and health care.
The next steps in this research work are oriented towards the construction of an annotated database of pressure ulcer 2D and 3D images accompanied with clinical metadata to foster the investigation in this field.
Publication details:
Zahia, S., García Zapirain, M.B., Sevillano, X., González, A., Kim, P.J. & Elmaghraby, A. (2020) Pressure injury image analysis with machine learning techniques: A systematic review on previous and possible future methods. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0933365718307127
This work has been funded by Aristos Campus Mundus (ACM) with references ACM2017_09, ACM2018_21 and ACM2019_14.
